Adrienne Buller on greenwashing, high finance, and the failures of capitalism viz the environment, in "The Value of a Whale".
This is a very earnest book by what seems to be an environmental activist about the mistaken notion that capitalism gives a fig about climate change. Buller goes through the painstaking economic rationales by which economists attempt to value or really, discount the value of, future generations. And how poorly carbon taxes have performed. And how feckless corporations are about their climate pledges, carbon offsets, and general greenwashing. And how unlikely it is that "socially conscious" investing will change anything. It is a frustrated, head-banging exercise in deflating illusions of economic theory and corporate responsibility. Skimming through it is perhaps the best approach. Here is a sample quote from Buller's conclusion:
Given this entrenched perspective, it is unsurprising that resistance to the kinds of bold change we need to secure a habitable planetary future for all and a safe present for many tend to focus on what we stand to lose. Undeniably, available evidence suggests that 'addressing environmental breakdown may require direct downscaling of economic production and consumption in wealthier countries'. This is an uncomfortable idea to grapple with, but as philosopher Kate Soper writes: 'If we have cosmopolitan care for the well-being of the poor of the world, and a concern about the quality of life for future generations, then we have to campaign for a change of attitudes to work, consumption, pleasure, and self-realization in affluent communities.' There is a sense that this future is necessarily austerian, anti-progress, and defined by lack. Indeed, the same media study cited above found discussion of economies defined by the absence of growth to focus on bleakness and stagnation. Comparatively little attention is directed at what we stand to gain - but there is much to be gained. Understanding what requires us to ask what the existing system currently fails to provide, from universal access to health case and education, to basic material security, to free time. It certainly does not offer a secure planetary future, let alone one in which all life can thrive. And it does not offer genuine democracy, justice or freedom for most. Absent these, what purpose is 'the economy' meant to serve?
Unfortunately, the book is not very economically literate either, making its illusions something of a village of straw men. Who ever thought that Royal Dutch Shell was going to solve climate change? Who ever thought that a $5 dollar per ton tax on CO2 emissions was going to accomplish anything? And who ever thought that the only reason to address climate heating was to save ourselves a dollar in 2098? All these premises and ideas are absurd, hardly the stuff of serious economic or social analysis.
But then, nothing about our approach to climate heating is serious. It is a psychodrama of capitalism in denial, composed of cossetted capitalist people in the five stages of grief over our glorious carbon-hogging culture. Trucks, guns, and drive-through hamburgers, please! Outright denial is only slowly ebbing away, as we sidle into the anger phase. The conservative Right, which mixes an apocalyptically destructive anti-conservative environmental attitude with a futile cultural conservatism, is angry now about everything. The idea that the environment itself is changing, and requires fundamental cultural and economic change, is an affront. The eco-conscious left is happy to peddle nostrums that nothing really has to change, if we just put up enough solar panels and fund enough green jobs.
Objectively, given the heating we are already experiencing and the much worse heating that lies ahead, we are not facing up to this challenge. It is understandable to not want to face change, especially limits to our wealth, freedoms, and profligacy. But we shouldn't blame corporations for it. The capitalist system exists to reflect our desires and fulfill them. If we want to binge-watch horror TV, it gives us that. If we want to gamble in Las Vegas, it gives us that. If we want to drive all around the country, it makes that possible. Capitalism transmutes whatever resources are lying around (immigrant labor, publically funded research, buried minerals and carbon, etc.) to furnish things we want. We can't blame that system for fouling up the environment when we knew exactly what was going on and wanted those things it gave us, every step of the way.
No, there is another mechanism to address big problems like climate heating, and that is government. That is where we can express far-sighted desires. Not the desire for faster internet or more entertaining TV, but deep and far-reaching desires for a livable future world, filled with at least some of the animals that we grew up with, and maybe not filled with plastic. It is through our enlightened government that we make the rules that run the capitalist system. Which system is totally dependent on, and subservient to, our collective wisdom as expressed through government.
So the problem is not that capitalism is maliciously ruining our climate, but that our government, representative as it is of our desires, has not fully faced up to the climate issue either. Because we, as a culture, are, despite the blaring warnings coming from the weather, and from scientists, don't want to hear it. There is also the problem that we have allowed the capitalists of our culture far too much say in the media and in government- a nexus that is fundamentally corrupt and distorts the proper hierarchy of powers we deserve as citizens.
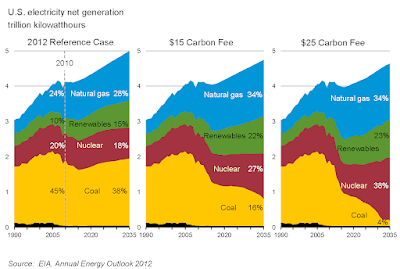 |
| The US games out in 2012 how various carbon taxes will affect emissions, given by electricity production. These are modest levels of taxation, and have modest effects. To actually address the climate crisis, a whole other magnitude of taxation and other tools need to be brought to bear. The actual trajectory came out to more renewables, no growth for nuclear power, and we are still burning coal. |
Let me touch on just one topic from the book- carbon taxes. This is classic case of squeemish policy-making. While it is not always obvious that carbon pricing would be a more fair or effective approach than direct regulation of the most offensive industries and practices, it is obvious that putting a price on carbon emissions can be an effective policy tool for reducing overall emissions. The question is- how high should that price be to have the effect we want? Well, due to the universal economic consensus that carbon pricing would be a good thing, many jurisdictions have set up such pricing or capping schemes. But very few are effective, because, lo and behold, they did not want to actually have a strong effect. That is, they did not want to disrupt the current way of doing things, but only make themselves (and ourselves) feel good, with a slight inducement to moderate future change. Thus they typically exempt the most polluting industries outright, and set the caps high and the prices low, so as not to upset anyone. And then Adrienne Buller wonders why these schemes are so universally ineffective.
Carbon prices in California are currently around $30 per ton CO2, and this has, according to those studying the system, motivated one third of the state's overall carbon reductions over the current decade. That is not terrible, but clearly insufficient, even for a forward-thinking state, since we need to wring carbon out of our systems at a faster pace. Raising that price would be the most direct way for us as a society to do that. But do we want to? At that point, we need to look in the mirror and ask whether the point of our policies should be addressing climate heating in the most effective way possible, or to avoid pain and change to our current systems. Right now, we are on a sort of optimal trajectory to avoid most of the economic and social pain of truly addressing climate change, (by using gradualist and incremental policies), but at the cost of not getting there soon enough and thus incurring increasing levels of pain from climate heating itself- now, and in a future that is measured, not in years, but in centuries.
The second big point to make about this book and similar discussions is that it largely frames the problem as an economic one for humanity. How much cost do we bear in 2100 and 2200, compared with the cost we are willing to pay today? Well, that really ignores a great deal, for there are other species on the planet than ourselves. And there are other values we have as humans, than economic ones. This means that any cost accounting that gets translated into a carbon price needs to be amplified several fold to truly address the vast array of harms we are foisting on the biosphere. Coral reefs are breaking down, tropical forests are losing their regenerative capability, and the arctic is rapidly turning temperate. These are huge changes and harms, which no accounting from an economic perspective "internalizes".
So, we need to psychologically progress, skipping a few steps to the facing-it part of the process, which then will naturally lead us towards truly effective solutions to get to carbon neutrality rapidly. Will it cost a lot? Absolutely. Will we suffer imbalances and loss of comforts? Absolutely. But once America faces up to a problem, we tend to do a good job accepting those tradeoffs and figuring out how to get the results we want.
- An earth systems perspective.
- I hope you are appreciating this free-range, hand-made, artisanal prose.
- Loneliness.
- Plastic is a thing too.
- Natural gas and the future of Europe.
- Maybe having cars parked everywhere isn't the best idea.
- Thoughts on the drug war.